Current Phylogenetic Analyses Include Which of the Following
D Identifying evolutionary sequences. Figure 1 shows a consensus of the trees obtained by the different methods trees are supplied as Supplementary Figures.

Phylogeny An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
An ordinary analysis today requires an author to rationalize the choice of taxa under study the choice of primary data the method of character coding including difficult issues of alignment.
. SINE bias Which of the following is not a limitation of the fossil record. Information on visible similarities only b. Steps in Phylogenetic Analysis The basic steps in any phylogenetic analysis include.
Which of the following statements about phylogenies is true. Which of the following phylogenies are equivalent. A sea squirt is thought to be more closely related to vertebrates than once thought because both vertebrate embryos and sea squirt larvae have notochords.
Rotating lineages around nodes changes the meaning of the information contained within the phylogenetic tree. Assessing phylogenetic signal 3. DNA sequences of interest can be retrieved using NCBI BLAST or similar search tools.
Taxa cannot be placed within other taxa. Assemble and align a dataset The first step is to identify a protein or DNA sequence of interest and assemble a dataset consisting of other related sequences. Dolphins Which of the following organisms likely has the most Hox genes.
Choosing methods for phylogenetic analysis 4. Photo 2 A and B The phylogenetic tree shown in below is based on photo 3 DNA sequences of just the viruses at the tips of the tree. 9 Topology of a tree is the branching pattern of a tree.
A Distinguishing between competing hypotheses. 9 After the branching event one taxon sequence can undergo more mutations then the other taxon. Information regarding how to classify organisms on the basis of external morphological characteristics and visible behaviors c.
We used three different methods of phylogenetic reconstruction. Current phylogenetic analyses include which of the following. Does it possess any of the characteristics listed in Table 1 on the following page.
6 and by the comparison of the PhyloPhlAn 30 approach of. The bone structure differences between species b. This evolutionary history or phylogeny is ideally represented as a binary tree.
We use Bayesian inference BI and maximum likelihood ML phylogenetic analyses of multilocus DNA sequence data to test current species hypotheses re-examine the phylogenetic position of the genus within the Lecanoromycetes and assess the phylogenetic position of the strictly parasitic Arthrorhaphis species in relation to the finally. The study of phylogeny the branching sequence of evolution aims to determine the evolutionary relationships between phyla. The five basic steps in phylogenetic analysis of sequences Hillis et al 1993 organized as shown in Figure 131 consist of.
Houston Chuanzhu Fan 2 Jenny Qiu-Yun Xiang Jan-Michael Schulze Rudolf Jung and. To distinguish between them the phylogenetic analysis must include at least one outgroup this being a homologous gene that we know is less closely related to A B Cand Dthan these four genes are to each other. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Morphological Data 1.
Scientists develop phylogenetic trees which serve as hypotheses about which species have evolved from which ancestors. Which of the following are traits that can be used to make a phylogenetic tree. This is achieved while maintaining high phylogenetic accuracy as shown by previous clade-specific analyses focusing on organisms from the human microbiome 41 by the overall consistency of the PhyloPhlAn tree with the current reference prokaryotic tree-of-life 26 Supplementary Fig.
Phylogenetic Analyses Identify 10 Classes of the Protein Disulfide Isomerase Family in Plants Including Single-Domain Protein Disulfide Isomerase-Related Proteins 1 w Norma L. Construction of optimal phylogenetic tree 5. Examine a flatworm specimen which we will use as the outgroup for this analysis.
When preparing a phylogenetic analysis any heritable genetic morphological physiological developmental or behavioral feature that varies among the groups to be studied is called a __________. C Determining the precise time when an evolutionary event occurred. B Determining whether trait evolution involved homologous or homoplastic changes.
For phylogenomic analyses 171 plastid genomes 152 species and five varieties were included representing one genus from myrtaceae and 42 genera from major lineages of melastomataceae sonerileaedissochaeteae 23 astronieae 1 bertolonieae 1 blakeeae 1 cyphostyleae 1 henrietteeae 1 kibessieae 1 marcetieae 1 melastomateae. Which of the following can NOT be used for phylogenetic analysis. E Testing hypotheses about species.
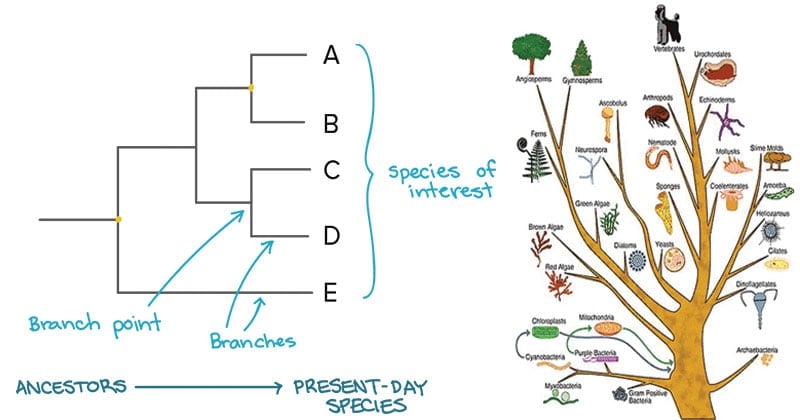
Currently most biologists divide the animal kingdom into 35 to 40 phyla. Phylogenetics is the systematic study of reconstructing the past evolutionary history of extant species or taxa based on present-day data such as morphologies or molecular information sequence data. Information from a range of sources including morphological genetic and biochemical data.
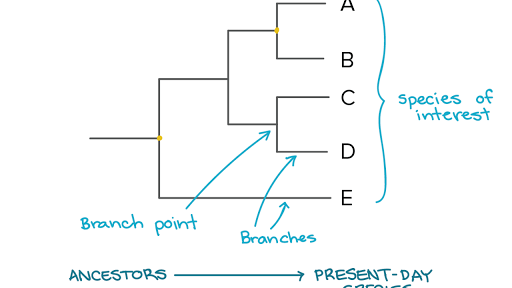
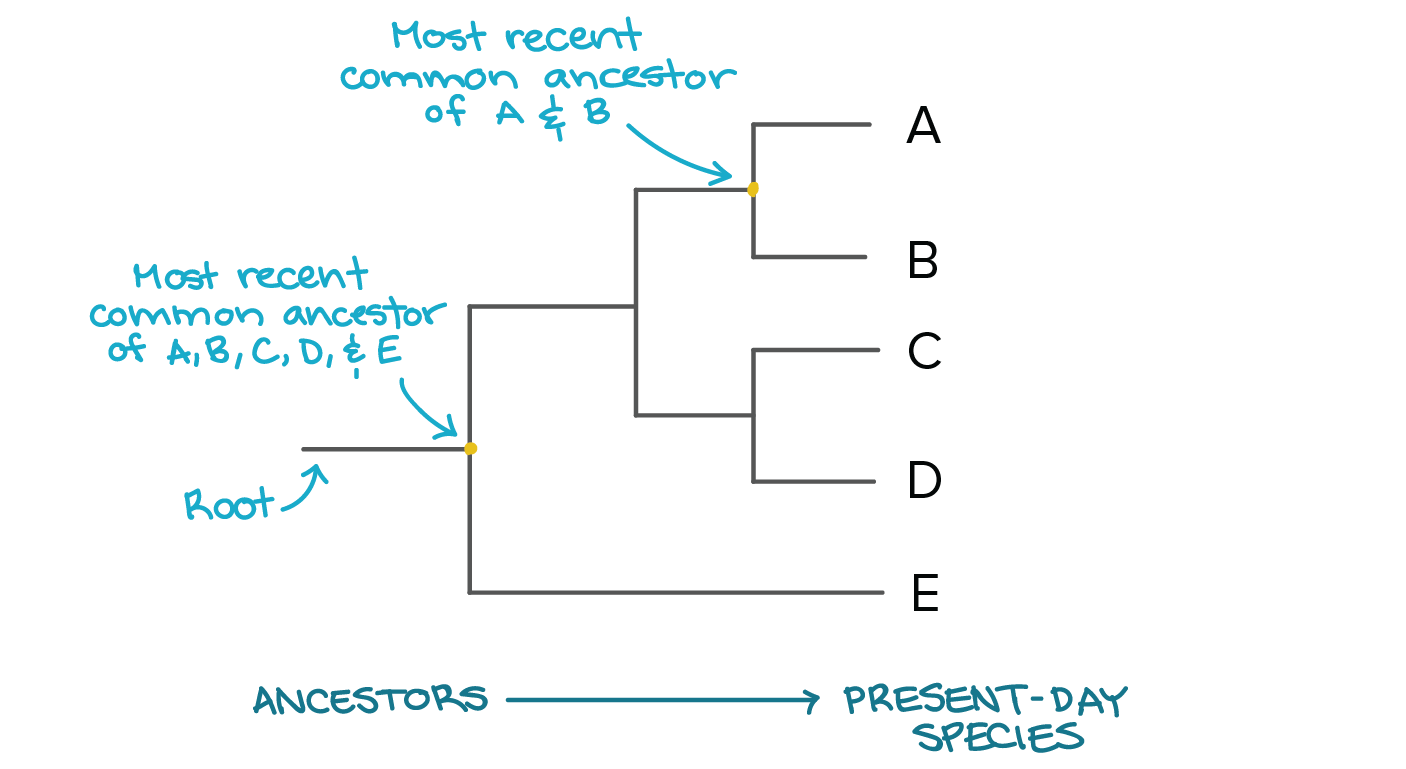
A phylogenetic tree is a diagram that represents evolutionary relationships among organisms. The phylogenetic analysis can only estimate the of changes that occurred from the time of separation. In trees two species are more related if they have a more recent.
All of the above. Phylogenetic trees are hypotheses not definitive facts. Maximum parsimony MP maximum likelihood ML quartet puzzling and a Bayesian phylogenetic inference approach as described in the Experimental Procedures.
Examine specimens of the other 12 species and indicate whether each possesses any of the derived. The outgroup enables the root of the tree to be located and the correct evolutionary pathway to be identified. The pattern of branching in a phylogenetic tree reflects how species or other groups evolved from a series of common ancestors.
The evolutionary distance between clades can be determined by examining the vertical distance between them.

Phylogenetic Trees Evolutionary Tree Article Khan Academy

Phylogenetic Tree Diagram Quizlet
Comments
Post a Comment